
New research reveals that while people struggle to distinguish between human and AI-generated voices, their brain responses differ significantly.
People assume happy voices to be real and ‘neutral’ voices to be AI.
Research shows that people struggle to identify AI from human voices, but their brain activities differ, suggesting unique responses to each voice type, which has significant implications for technology and ethics.
AI Voice Recognition
People are not very good at distinguishing between human voices and voices generated by <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]” tabindex=”0″ role=”link”>artificial intelligence (AI), but our brains do respond differently to human and AI voices. This is according to research to be presented on June 25 at the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) Forum 2024.[1]
The study will be presented by doctoral researcher Christine Skjegstad, and carried out by Ms Skjegstad and Professor Sascha Frühholz, both from the Department of Psychology at the <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]” tabindex=”0″ role=”link”>University of Oslo (UiO), Norway.
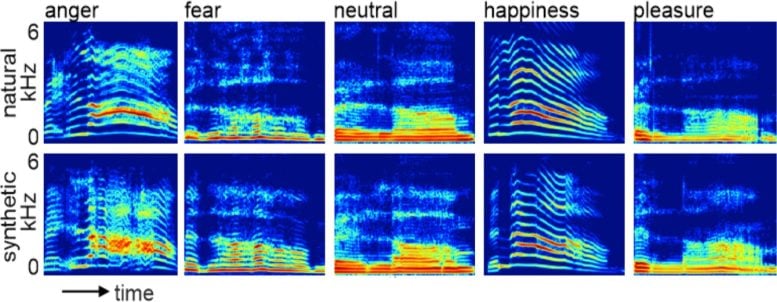
Spectrograms to demonstrate the similarity between human and AI voices. Credit: FENS Forum / Christine Skjegstad
Advancements and Challenges in AI Voice Technology
Ms Skjegstad said: “We already know that AI-generated voices have become so advanced that they are nearly indistinguishable from real human voices. It’s now possible to clone a person’s voice from just a few seconds of recording, and scammers have used this technology to mimic a loved one in distress and trick victims into transferring money. While <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]” tabindex=”0″ role=”link”>machine learning experts have been developing technological solutions to detect AI voices, much less is known about the human brain’s response to these voices.”
The research involved 43 people who were asked to listen to human and AI-generated voices expressing five different emotions: neutral, angry, fear, happy, pleasure.[2] They were asked to identify the voices as synthetic or natural while their brains were studied using functional magnetic resonance imaging (<span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]” tabindex=”0″ role=”link”>fMRI). fMRI is used to detect changes to blood flow within the brain, indicating which parts of the brain are active. The participants were also asked to rate the characteristics of the voices they heard in terms of naturalness, trustworthiness, and authenticity.
Participant Performance in Voice Identification
Participants correctly identified human voices only 56% of the time and AI voices 50.5% of the time, meaning they were equally bad at identifying both types of voices.
People were more likely to correctly identify a ‘neutral’ AI voice as AI (75% compared to 23% who could correctly identify a neutral human voice as human), suggesting that people assume neutral voices are more AI-like. Female AI neutral voices were identified correctly more often than male AI neutral voices. For happy human voices, the correct identification rate was 78%, compared to only 32% for happy AI voices, suggesting that people associate happiness as more human-like.
Both AI and human neutral voices were perceived as least natural, trustworthy, and authentic while human happy voices were perceived as most natural, trustworthy, and authentic.
Brain Response Differences to Human and AI Voices
However, looking at the brain imaging, researchers found that human voices elicited stronger responses in areas of the brain associated with memory (right hippocampus) and empathy (right inferior frontal gyrus). AI voices elicited stronger responses in areas related to error detection (right anterior mid cingulate cortex) and attention regulation (right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex).
Ms Skjegstad said: “My research indicates that we are not very accurate in identifying whether a voice is human or AI-generated. The participants also often expressed how difficult it was for them to tell the difference between the voices. This suggests that current AI voice technology can mimic human voices to a point where it is difficult for people to reliably tell them apart.
“The results also indicate a bias in perception where neutral voices were more likely to be identified as AI-generated and happy voices were more likely to be identified as more human, regardless of whether they actually were. This was especially the case for neutral female AI voices, which may be because we are familiar with female voice assistants such as Siri and Alexa.
“While we are not very good at identifying human from AI voices, there does seem to be a difference in the brain’s response. AI voices may elicit heightened alertness while human voices may elicit a sense of relatedness.”
The researchers now plan to study whether personality traits, for example extraversion or empathy, make people more or less sensitive to noticing the differences between human and AI voices.
Expert Opinion and Broader Implications
Professor Richard Roche is chair of the FENS Forum communication committee and Deputy Head of the Department of Psychology at Maynooth University, Maynooth, County Kildare, Ireland, and was not involved in the research. He said: “Investigating the brain’s responses to AI voices is crucial as this technology continues to advance. This research will help us to understand the potential cognitive and social implications of AI voice technology, which may support policies and ethical guidelines.
“The risks of this technology being used to scam and fool people are obvious. However, there are potential benefits as well, such as providing voice replacements for people who have lost their natural voice. AI voices could also be used in therapy for some mental health conditions.”
Notes
- PS07-29AM-602, “Neural dynamics of processing natural and digital emotional vocalisation” by Christine Skjegstad, Poster Session 07 – Late-Breaking Abstracts, Saturday, 29 June, 09:30-13:00, Poster area, https://fens2024.abstractserver.com/program/#/details/presentations/4774
- Since submitting their abstract, the researchers have included additional data in their analyses.
Funding: The Department of Psychology at the University of Oslo (UiO)

